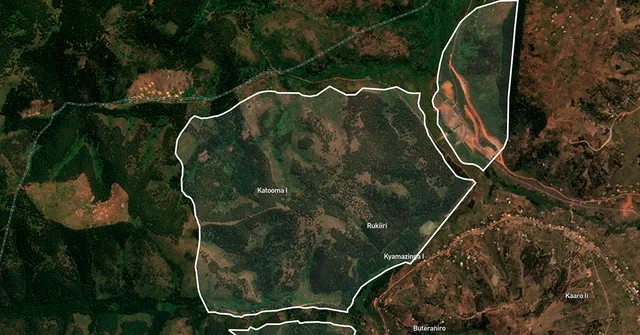
BeZero Carbon has unveiled what it describes as the most comprehensive spatial dataset ever created for the voluntary carbon market, mapping more than 3,000 nature-based carbon offset projects across 20 international registries. The BeZero Global Boundaries Database, launched on 30 October 2025, aims to resolve long-standing issues around data fragmentation, inconsistent boundaries, and the risk of double-counting in carbon credit reporting.
According to BeZero, the database consolidates thousands of project boundaries into a harmonised global layer, offering detailed metadata such as project status, type, and location. The data show that around 34% of projects are active and registered, 42% remain in development, and 24% have been completed, withdrawn, or made inactive.
The London-based climate ratings firm said its team manually digitised over 600 projects for which digital boundaries were previously unavailable, significantly enhancing data completeness. The analysis also found that roughly 10% of projects have boundary overlaps, a discovery that could help project developers and verifiers correct double-counting or leakage issues before certification.
Beyond transparency, BeZero’s geospatial data enable investors and regulators to benchmark spatial risks such as wildfire exposure in forest management projects or land-use conflicts in emerging offset markets. The firm said such insights are key to “strengthening the integrity and decision-making framework” of the voluntary carbon market.
The Global Boundaries Database is now integrated into BeZero’s analytics platform and available for institutional users. It is also being used by leading research partners, including the Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research and the University of Cambridge, to advance scientific and policy studies.